| easyexcel导出excel自定义合并单元格【动态表头和动态数据均可以自由合并】 | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › excel 合并数据表 › easyexcel导出excel自定义合并单元格【动态表头和动态数据均可以自由合并】 |
easyexcel导出excel自定义合并单元格【动态表头和动态数据均可以自由合并】
|
网上合并单元格的博客还是很多的,大家自行舍取吧。本文主要讲解固定与不固定的表头和内容如何合并 参考官网 https://easyexcel.opensource.alibaba.com/docs/current/quickstart/write 导包 com.alibaba easyexcel 3.1.3 一 固定表头、固定内容 1 先看看效果假如我们要这样的效果,统计某个小区每户的水电煤费用【假设小区的楼栋格局一样,不一样的我们做动态处理】 这里先假设一个小区两栋楼,每栋楼三户人家【实际肯定比这个多,不要抬杠】 表头和内容都没合并前 都合并后 这里重点讲解下 @ExcelProperty({“2020年”, “1月”}) 用来合并表头的,数组第一个看作excel的第一行,数组第二个看着excel第二行。自动合并头,头中相同的字段上下左右都会去尝试匹配(前提automaticMergeHead属性没有设置成fasle)默认true。 假如有分级别表头合并,不分级别合并的表头写字符串也行,写数组也行,比如这样一样的效果@ExcelProperty({“小区”, “小区”})@ContentLoopMerge(eachRow = 3) 用来合并内容的,有两个属性eachRow = 3(每3行合并);columnExtend列偏移,假如我们在房间号上面写个@ContentLoopMerge(eachRow = 3, columnExtend = 2) 效果如下,列偏移2就是合并两列,这两个属性单独用就是合并行或者列,合在一起用就是同时合并行和列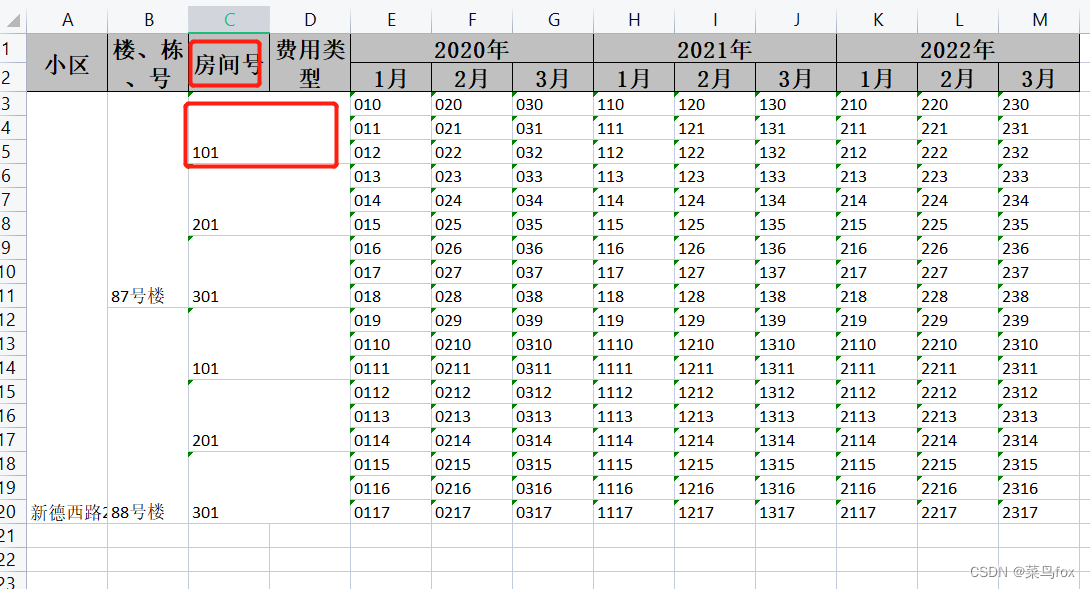 另外一种单独合并列的,在year0v1字段上加@ContentLoopMerge(columnExtend = 2),效果如下 另外一种单独合并列的,在year0v1字段上加@ContentLoopMerge(columnExtend = 2),效果如下 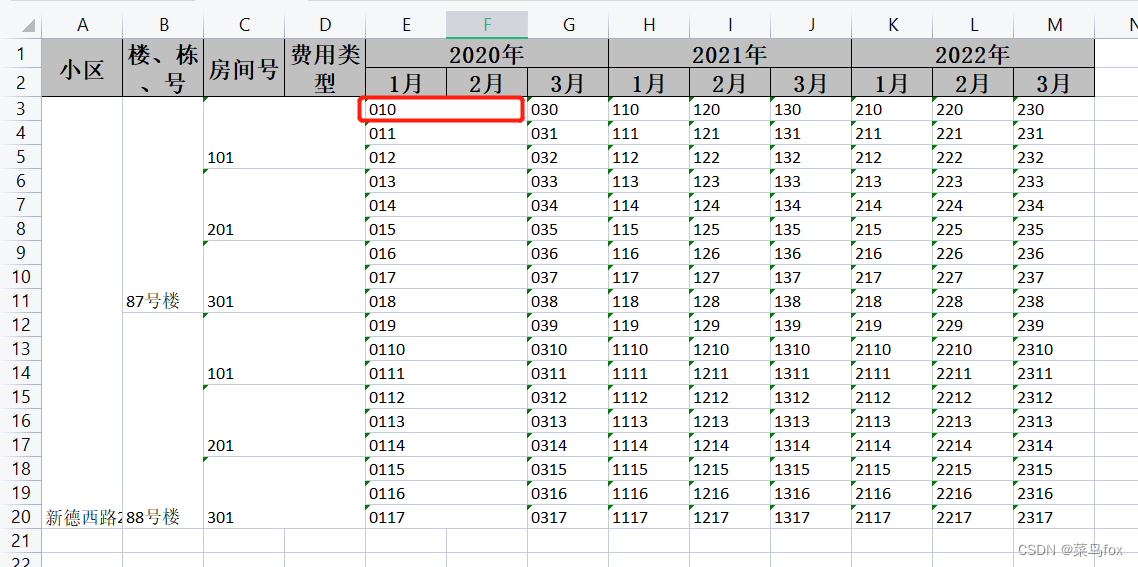 不能实现下面这种,同一个字段,一会儿合并行,一会合并列【我接到的需求就是这样,苦涩.jpg】 不能实现下面这种,同一个字段,一会儿合并行,一会合并列【我接到的需求就是这样,苦涩.jpg】  二 动态表头、动态内容
二 动态表头、动态内容
动态表头和内容,主要是不依赖实体了,表头合并可以利用automaticMergeHead自动合并表头,也可以利用poi的CellRangeAddress实现自定义合并规则 1 先看效果表头和数据效果,假如每个月份只要当前月份及以前的数据,那么月份字段就是动态变化的了,这个时候用实体就会麻烦些 
这个是代码导出来没有合并表头和内容的效果
CellRangeAddress构造函数也可以合并表头,只要修改合并下标即可,但表头依旧建议用.head()来处理 2 代码组装数据的部分大家不用看了,直接看合并策略即可 package cn.fox.mydemo.easyexcel; import cn.fox.mydemo.easyexcel.vo.Vo1; import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel; import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.List; public class MyTest { @Test public void dongtai() { String fileName = "D:\\" + System.currentTimeMillis() + ".xlsx"; List cellRangeAddressList = new ArrayList(); // 内容合并策略 cellRangeAddressList.add(new CellRangeAddress(2,41,0,0)); cellRangeAddressList.add(new CellRangeAddress(2,14,1,1)); cellRangeAddressList.add(new CellRangeAddress(15,23,1,1)); cellRangeAddressList.add(new CellRangeAddress(24,40,1,1)); cellRangeAddressList.add(new CellRangeAddress(14,14,2,3)); cellRangeAddressList.add(new CellRangeAddress(23,23,2,3)); cellRangeAddressList.add(new CellRangeAddress(40,40,2,3)); cellRangeAddressList.add(new CellRangeAddress(41,41,1,3)); EasyExcel.write(fileName).head(getHeadList()) .sheet("小区水电煤费用汇总") // 自定义 合并策略 todo CommonMergeStrategy类在博客下面 .registerWriteHandler(new CommonMergeStrategy(cellRangeAddressList)) // .automaticMergeHead(false) // 设置是否自动合并表头,默认true .doWrite(getDongTaiDataList()); } private List getHeadList() { List resultList = new ArrayList(); // A 列 List lis0 = new ArrayList(); lis0.add("小区"); lis0.add("小区"); resultList.add(lis0); // B 列 List lis1 = new ArrayList(); lis1.add("楼、栋、号"); lis1.add("楼、栋、号"); resultList.add(lis1); // C 列 List lis2 = new ArrayList(); lis2.add("房间号"); lis2.add("房间号"); resultList.add(lis2); // D 列 List lis3 = new ArrayList(); lis3.add("费用类型"); lis3.add("费用类型"); resultList.add(lis3); // E 列 List lis4 = new ArrayList(); lis4.add("2023年"); lis4.add("1月"); resultList.add(lis4); // F 列 List lis5 = new ArrayList(); lis5.add("2023年"); lis5.add("2月"); resultList.add(lis5); // G 列 List lis6 = new ArrayList(); lis6.add("2023年"); lis6.add("3月"); resultList.add(lis6); return resultList; } private List getDongTaiDataList() { List resultList = new ArrayList(); List list = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i map.put("k2", "87号楼"); } else if (i map.put("k2", "89号楼"); } if (i % 20 map.put("k3", "201"); } else if (i % 20 map.put("k3", "401"); } else { map.put("k3", "501"); } if (i % 4 == 0) { map.put("k4", "水费"); } else if (i % 4 == 1) { map.put("k4", "电费"); } else if (i % 4 == 2) { map.put("k4", "煤气费"); } else if (i % 4 == 3) { map.put("k4", "总计"); } map.put("v1", "01" + i); map.put("v2", "02" + i); map.put("v3", "03" + i); // todo 如果到了4月份,就增加一个map.put("v4", "04" + i); 以此类推 list.add(map); } // 添加一条总计 getStringObjectLinkedHashMap(list, "87号楼", 12); getStringObjectLinkedHashMap(list, "88号楼", 21); getStringObjectLinkedHashMap(list, "89号楼", 38); getStringObjectLinkedHashMap(list, "总计", 0); // 把List转成List for (HashMap hm : list) { List lis = new ArrayList(); for (String key : hm.keySet()) { lis.add(String.valueOf(hm.get(key))); } resultList.add(lis); } return resultList; } private void getStringObjectLinkedHashMap(List list, String lou, int index) { LinkedHashMap map1 = new LinkedHashMap(); map1.put("k1", "新德西路207弄"); map1.put("k2", lou); map1.put("k3", "总计"); map1.put("k4", "总计"); map1.put("v1", "01"); map1.put("v2", "02"); map1.put("v3", "03"); if (index == 0) { list.add(map1); } else { list.add(index, map1); } } } 三 优劣汇总、工具类汇总 优点缺点固定实现容易不够灵活动态非常灵活实现困难(需要计算合并下标) 四 封装好的工具类调用工具类 @GetMapping("downLoadList") public void downLoadList(HttpServletResponse response) { EasyExcelUtil.simpleWrite(new CommonWriteEntity(response, "小区水电煤费用汇总", getHeadList(), getDongTaiDataList(), cellRangeAddressList)); }CommonWriteEntity package cn.fox.mydemo.easyexcel; import lombok.Data; import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.util.List; /** * 公共写excel实体 */ @Data public class CommonWriteEntity { /** * 响应流 */ private HttpServletResponse response; /** * sheet名字 */ private String sheetName; /** * 动态表头list【只适用一行表头】 */ private List beforeHeadList; /** * 动态表头list【适用多行行表头】 */ private List headList; /** * 数据list */ private List dataList; /** * clazz */ private Class clazz; /** * 合并单元格策略,基于poi实现 */ private List cellRangeAddressList; /** * todo 根据实际需求,自行添加构造方法 * * @param response 响应流 * @param sheetName sheet名字 * @param beforeHeadList 动态表头list * @param dataList 数据list * @param clazz clazz */ public CommonWriteEntity(HttpServletResponse response, String sheetName, List beforeHeadList, List dataList, Class clazz) { this.response = response; this.sheetName = sheetName; this.beforeHeadList = beforeHeadList; this.dataList = dataList; this.clazz = clazz; } public CommonWriteEntity(HttpServletResponse response, String sheetName, List headList, List dataList, List cellRangeAddressList) { this.response = response; this.sheetName = sheetName; this.headList = headList; this.dataList = dataList; this.cellRangeAddressList = cellRangeAddressList; } } }CommonMergeStrategy package cn.fox.mydemo.easyexcel; import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Head; import com.alibaba.excel.write.merge.AbstractMergeStrategy; import org.apache.commons.collections4.CollectionUtils; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet; import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress; import java.util.List; /** * 公共的合并单元格类,支持自定义合并策略 */ public class CommonMergeStrategy extends AbstractMergeStrategy { // 合并策略list private List cellRangeAddresssList; // 通过有参数构造方法,设置合并策略 public CommonMergeStrategy(List list) { this.cellRangeAddresssList = list; } /** * 重写合并策略方法 * @param sheet sheet * @param cell cell * @param head head * @param relativeRowIndex relativeRowIndex */ @Override protected void merge(Sheet sheet, Cell cell, Head head, Integer relativeRowIndex) { // 将自定义合并策略假如excel if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(cellRangeAddresssList)) { // if (cell.getRowIndex() == 1 && cell.getColumnIndex() == 0) { for (CellRangeAddress item : cellRangeAddresssList) { sheet.addMergedRegionUnsafe(item); } // } } } }EasyExcelUtil package cn.fox.mydemo.easyexcel; import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel; import com.alibaba.excel.write.builder.ExcelWriterSheetBuilder; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; /** * excel工具类 */ @Slf4j public class EasyExcelUtil { /** * 写入excl * * @param commonWriteEntity 公共写excel实体 * @param */ public static void simpleWrite(CommonWriteEntity commonWriteEntity) { OutputStream outputStream = null; List headList = null; // 一维表头 换为 二维表头【如果没有,以clazz表头为准】 if (commonWriteEntity.getBeforeHeadList() != null && commonWriteEntity.getBeforeHeadList().size() > 0) { headList = getHeadList(commonWriteEntity.getBeforeHeadList()); } // 多行表头 if (commonWriteEntity.getHeadList() != null && commonWriteEntity.getHeadList().size() > 0) { headList = commonWriteEntity.getHeadList(); } try { outputStream = commonWriteEntity.getResponse().getOutputStream(); // 构建excelSheetbuilder ExcelWriterSheetBuilder sheetBuilder = EasyExcel.write(outputStream, commonWriteEntity.getClazz()) .head(headList).autoTrim(true).sheet(commonWriteEntity.getSheetName()); // 合并策略 if (commonWriteEntity.getCellRangeAddressList() != null && commonWriteEntity.getCellRangeAddressList().size() > 0) { sheetBuilder.registerWriteHandler(new CommonMergeStrategy(commonWriteEntity.getCellRangeAddressList())); } // 写入数据 sheetBuilder.doWrite(commonWriteEntity.getDataList()); outputStream.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { log.error(e.getMessage()); } finally { if (outputStream != null) { try { outputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { log.error(e1.getMessage()); } } } } /** * 将一维表头处理成 EasyExcel 需要的二维表头【只适用一行表头】 * * @param beforeHeadList 一维表头list * @return List> 二维表头 */ private static List getHeadList(List beforeHeadList) { List headList = new ArrayList(); if (beforeHeadList != null) { for (String head : beforeHeadList) { List cList = new ArrayList(); cList.add(head); headList.add(cList); } } return headList; } /** * 模板填充数据 * * @param response response * @param templateFile 模板文件 * @param map 数据 */ public static void fill(HttpServletResponse response, File templateFile, Map map) { OutputStream outputStream = null; try { outputStream = response.getOutputStream(); EasyExcel.write(response.getOutputStream()).withTemplate(templateFile).sheet().doFill(map); outputStream.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { log.error(e.getMessage()); } finally { if (outputStream != null) { try { outputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { log.error(e1.getMessage()); } } } } } |
【本文地址】
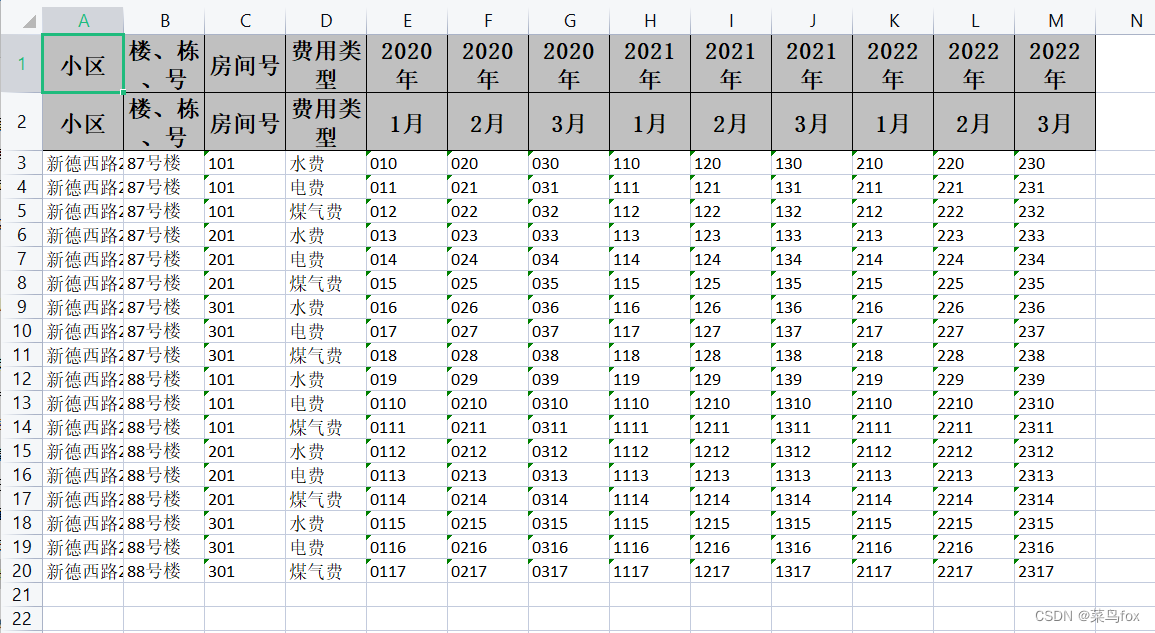
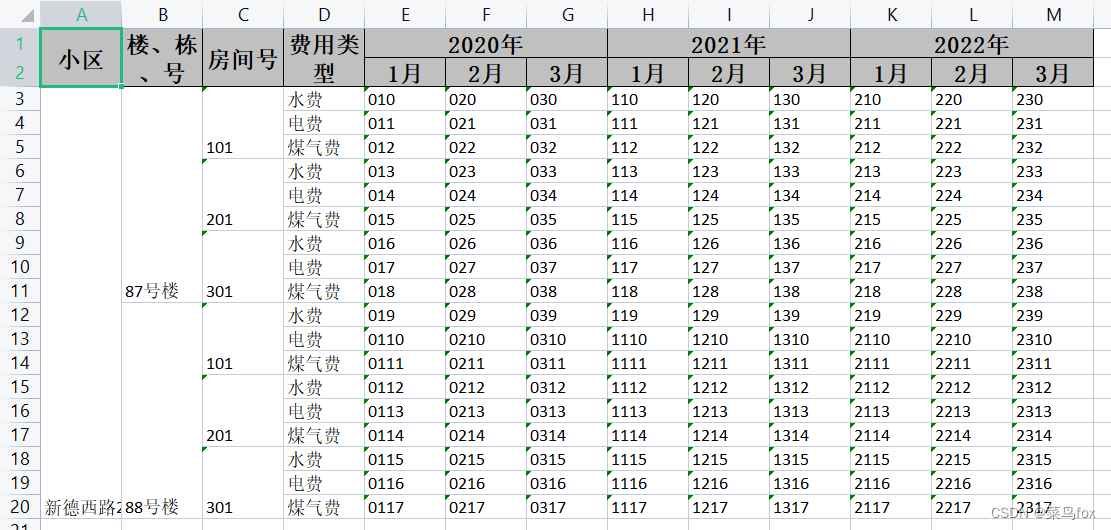
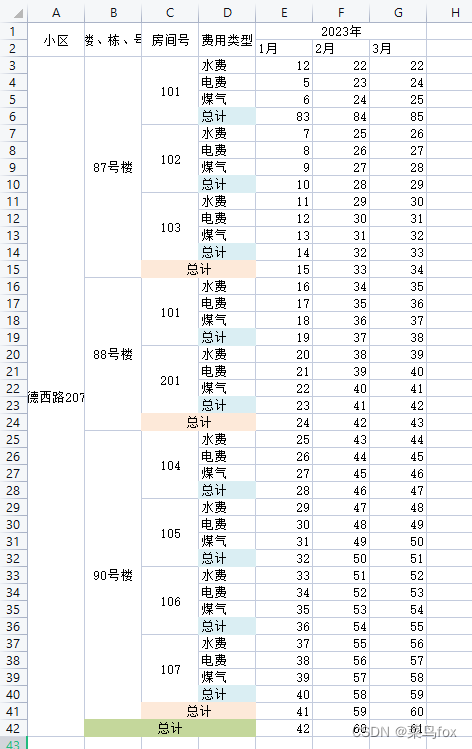
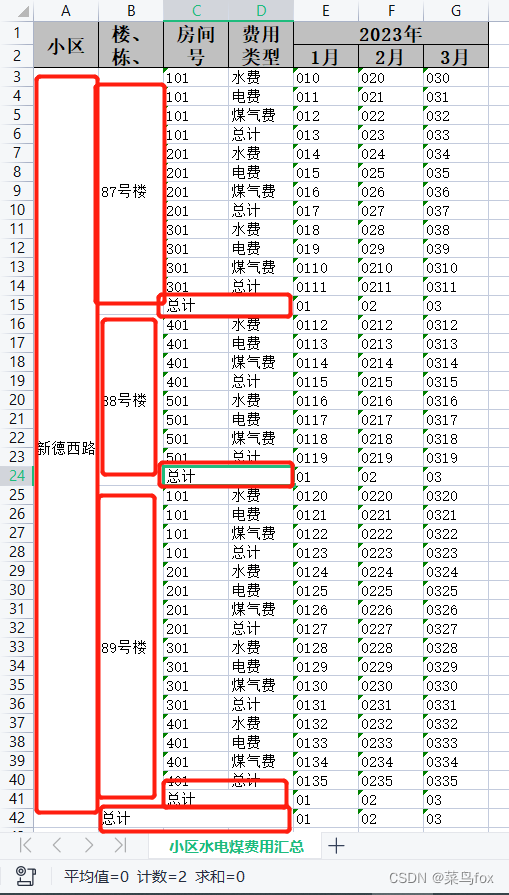
 问题是数据库出来的数据要么是List,要么是List,所以需要我们把List转成List,如果本身就是空值,可以用空串去填充,不然就串行了
问题是数据库出来的数据要么是List,要么是List,所以需要我们把List转成List,如果本身就是空值,可以用空串去填充,不然就串行了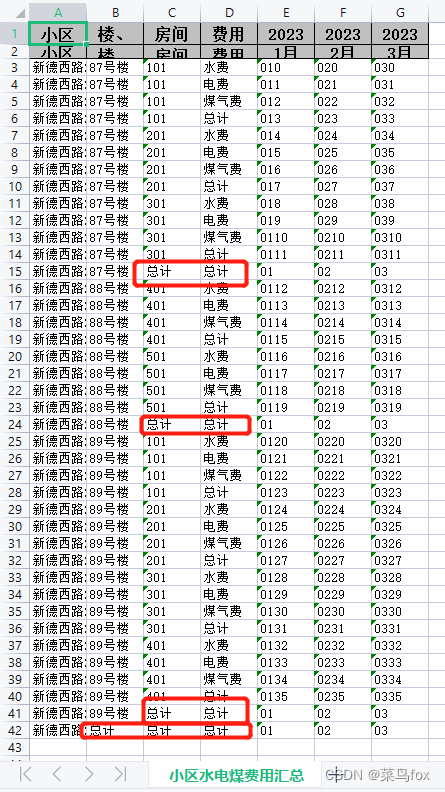 这是合并以后的效果 动态内容合并的方式非常多,这里讲解一种万能的(利用poi的CellRangeAddress实现) 合并策略有4个参数,分别是开始行,结束行,开始列,结束列。下标从0开始 CellRangeAddress(int firstRow, int lastRow, int firstCol, int lastCol)
这是合并以后的效果 动态内容合并的方式非常多,这里讲解一种万能的(利用poi的CellRangeAddress实现) 合并策略有4个参数,分别是开始行,结束行,开始列,结束列。下标从0开始 CellRangeAddress(int firstRow, int lastRow, int firstCol, int lastCol)